01 Hazards of strong acid (hydrochloric acid) corrosion
acid corrosion reaction:
2H++Fe Fe2++H2
When the coiled tubing is in contact with strong acid, an electrochemical reaction will occur, which will reduce the thickness of the coiled tubing wall in an acidic environment for a long time, reduce the tensile strength and fatigue life of the coiled tubing, and cause the coiled tubing to fail prematurely.
02 Strong acid corrosion during coiled tubing operation
In the process of coiled tubing acidizing operation, a certain amount of concentrated hydrochloric acid is often used. If the time is too long in the downhole, or if it is not cleaned in time after the operation, the residual acid will cause serious corrosion to the coiled tubing, resulting in the thinning of the coiled tubing wall thickness, leading to punctures and fractures which would have a huge impact on field operations.



03 Jason's simulation test on strong acid corrosion and suggestions for preventive measures
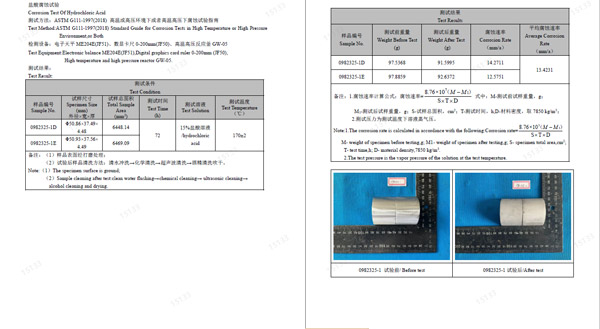
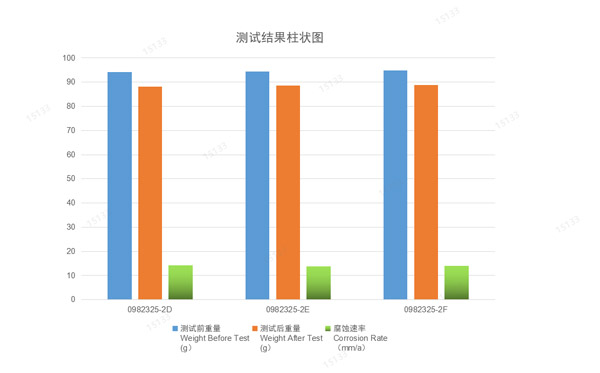
Aiming at the thinning of wall thickness and puncture caused by strong acid corrosion of coiled tubing during operation, the corrosion rate of coiled tubing in strong acid was obtained through the corrosion test under the simulating corrosion condition of hydrochloric acid, and corresponding preventive suggestions are provided as here below:
Simulated corrosion test:
Test standard:ASTM G111-1997(2013) Guidelines for corrosion in high temperature or high pressure environments, or under high temperature and pressure.
Corrosion condition:
170℃
15% concentrated hydrochloric acid
72hrs
preventive measures:
Ø Select a reasonable corrosion inhibitor to cooperate with acidizing operation;
Ø Before operation, carry out corrosion simulation test evaluation according to the type of operating acid and concentration ratio, especially pay attention to the influence of downhole temperature on the performance of corrosion inhibitor;
Ø During the operation, try to minimize the residence time of the tubing in the downhole, in order to reducing the corrosion time of the residual acid on the outer wall of the coiled tubing. At the same time, pay attention to the protection timeliness of corrosion inhibitors;
Ø After the operation, clean the tubing, neutralize the residual acid inside, and apply oil inside and outside for protection.



