Harm of oxygen corrosion
Although the maximal solubility of oxygen in water is only 8ppm, those of CO2 and H2S can reach as high as 800ppm and 400 ppm respectively. Oxygen is the most corrosive gas when moisture exists, so preventing oxygen from entering the system can effectively control oxygen corrosion.
The results show that the corrosion rate rank of O2, CO2, H2S in the same solution and temperature.
O2corrosion rate>CO2corrosion rate>H2S corrosion rate
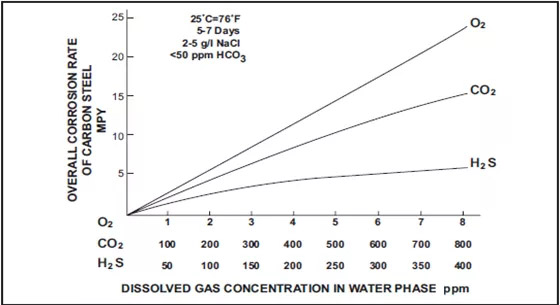
In addition, oxygen as a strong oxidant will highly affect the corrosion rate of CO2 and H2S. As the oxygen concentration increase, the corrosion rate of CO2 and H2S will significantly increase.
Circumstances under which coiled tubing is prone to oxygen corrosion
When coiled tubing is used for nitrogen gas lift operation in the field, membrane nitrogen is often used. The purity of membrane nitrogen is only maximum 95%, while it contains more than 5% oxygen. High flow rate oxygen reacts with moisture and base material of coiled tubing under the well with high temperature, producing ferric oxide hydrate, which are further decomposed to ferroferric oxide (flake and powder)in form of powder. The powder will even block the coiled tubing and seriously affect the operation under severe circumstance.

Coiled tubing clogging caused by ferric oxide scale
The characteristics of oxygen corroded pipes: Under different working conditions, there are different oxygen corrosion characteristics as follows:
· A uniform black-red rust layer;
· A great amount of scaly iron oxide, the cleaning of which will leave a surface with shallow dish-shaped pits;
· Corrosion pits with relatively smooth surface and shallow depth.
Jason Energy research on oxygen corrosion simulation experiment and suggestion of preventive measures
In order to study the rate and products of oxygen corrosion, Jason conducted the experimental study of nitrogen and oxygen corrosion under simulated similar conditions and the analysis of corrosion products, and put forward some preventive suggestions.
# Nitrogen and oxygen corrosion test under simulated conditions
· Test method: ASTM G111-1997(2018)
· Test solution:5% sodium chloride solution
· Test cycle:168h
· Test temperature: 150±2℃
· Gas pressure:95% nitrogen and 5% oxygen mixture,total pressure 10MPa
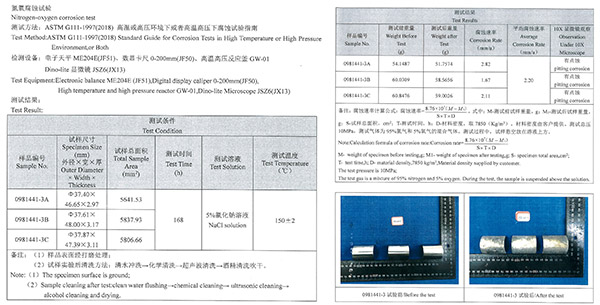
Nitrogen oxygen corrosion test report
Test results: The average corrosion rate of conventional carbon steel coiled tubing is about 2.20mm/a
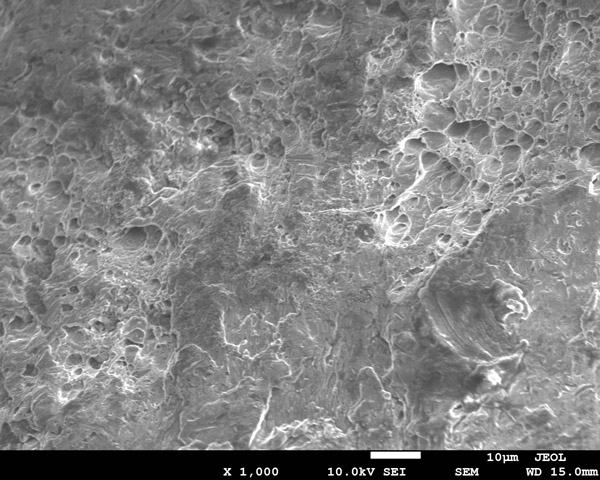
# Energy spectrum and XRD test report of oxygen corrosion products
According to the results, the corrosion products are mainly iron oxides, such as Fe₂O₃, Fe₃O₄.
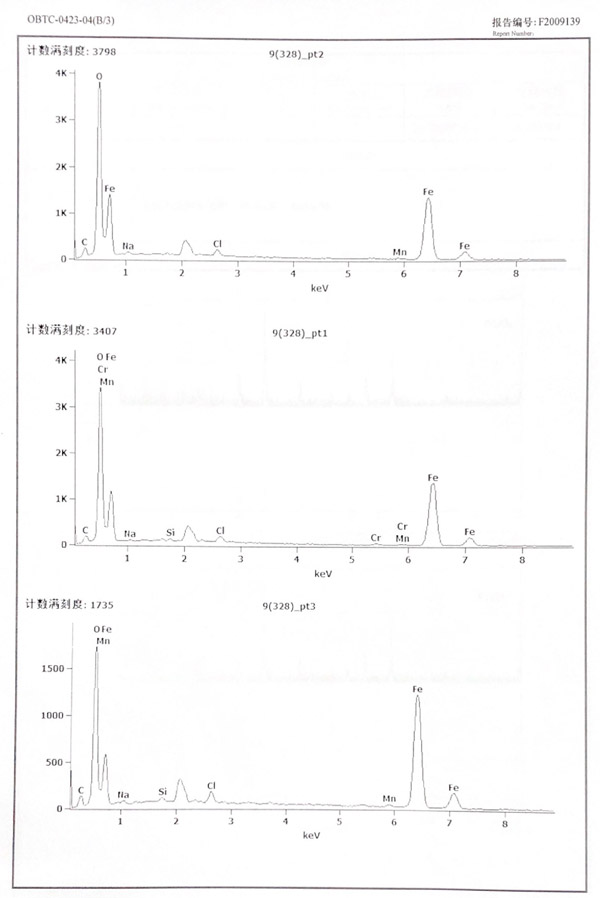
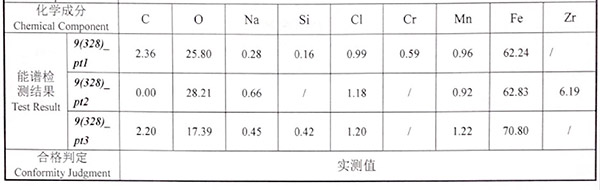
Energy spectrum test results
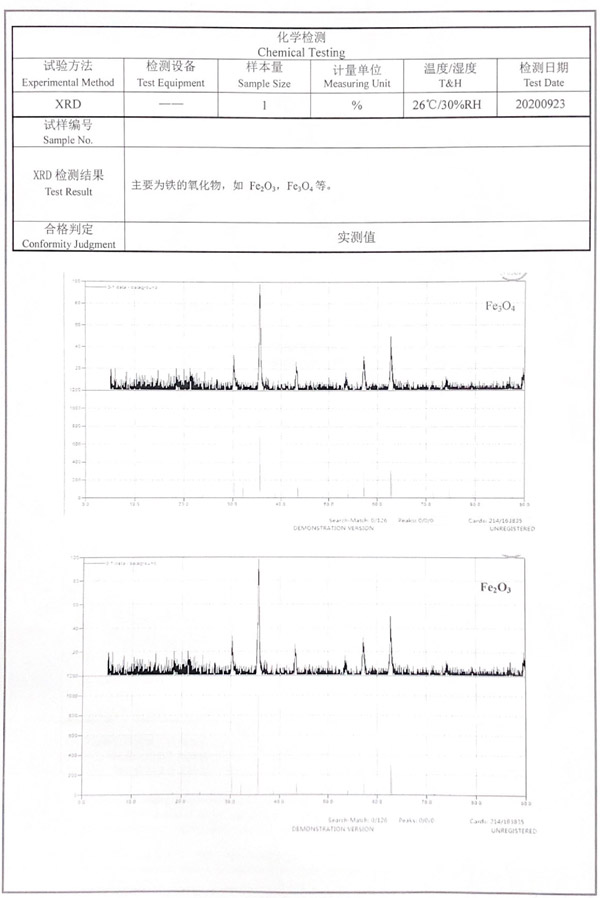
XRD test results
# Preventive measures of nitrogen oxygen corrosion
· The liquid nitrogen gas lift is used instead the membrane nitrogen to improve the nitrogen purity and eliminate the root of oxygen corrosion;
· In the process of coiled tubing operation, the corresponding inhibitor is injected to cooperate with the field operation of membrane nitrogen to reduce the oxygen corrosion rate;
· In maintenance after gas lift operation, clean the inside of the pipe and coat the inner surface of the pipe with oil for protection. In case of no operation for a long time, the pipe wall shall be coated with oil against corrosion, blown dry and filled with nitrogen, with its ends sealed and blocked;
· In the corrosive environment, shorten the staytime under the well as much as possible and reduce the exposure period;
· Use coiled tubing products of high alloy.



